Top 9 Zero Trust Security Solutions in 2026


Written by
John MartinezLast updated on:
October 17, 2025Reading time:
Contents
Built for Security. Loved by Devs.
- Free Trial — No Credit Card Needed
- Full Access to All Features
- Trusted by the Fortune 100, early startups, and everyone in between
Summary: Traditional access control solutions have an intrinsic design flaw: they operate with an assumption of trust. Zero trust is a security and authentication model that eliminates the assumption of trust and shifts the focus from a traditional security parameter, like a VPN or firewall, to the individual user. Nearly all (92 percent) cybersecurity professionals agree that it’s the best network security approach that exists. In this article, we’ll evaluate the top nine zero trust solutions and help you decide which is right for your organization.
1. StrongDM
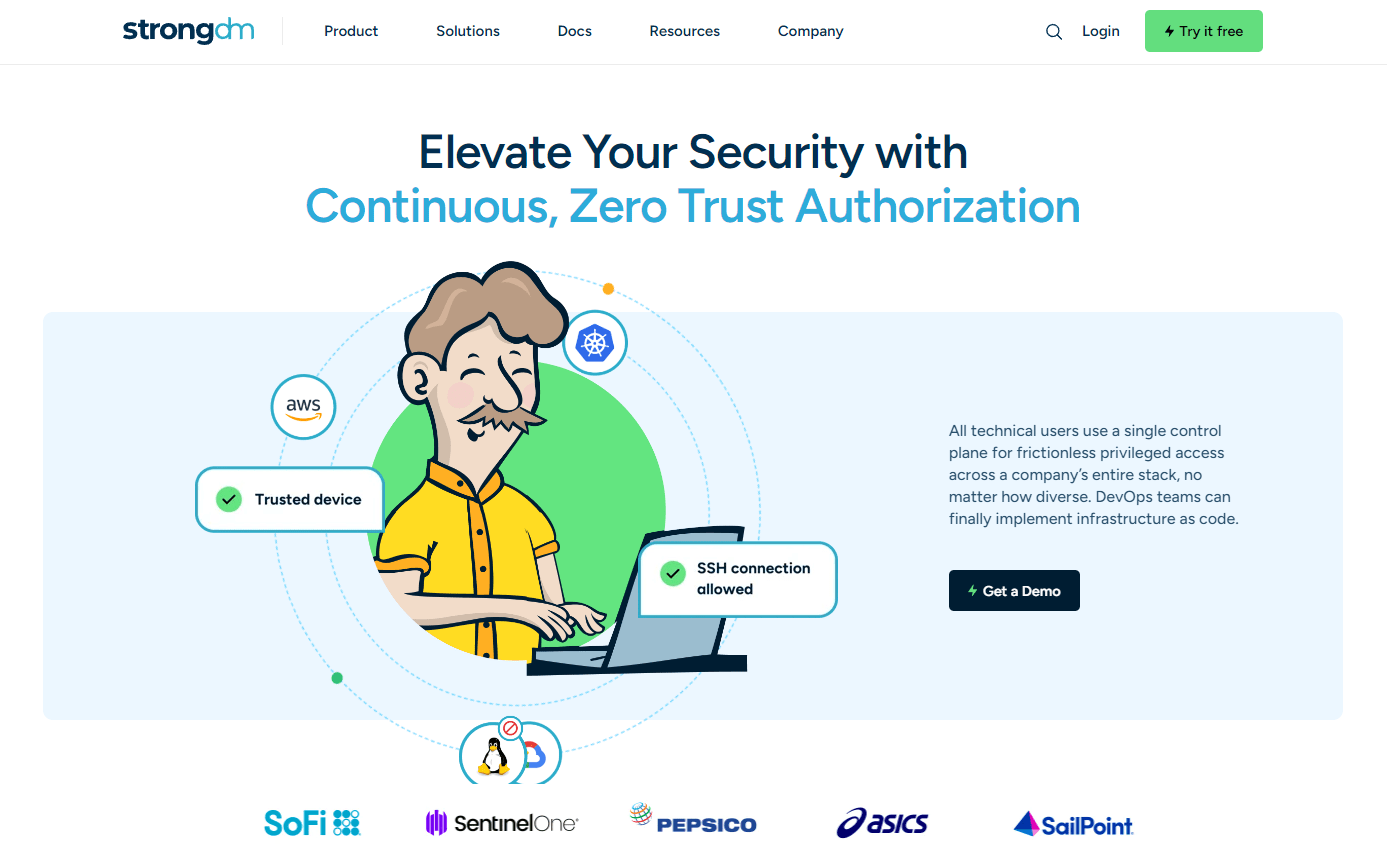
StrongDM's Continuous Zero Trust Authorization introduces dynamic, context-based security controls that evolve in tandem with potential threats, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and enabling stringent security without hindering productivity.
Continuous Zero Trust Authorization transforms the concept of security from a static, perimeter-based model to a dynamic, continuous, and context-aware system. This approach ensures that no entity, whether internal or external, is trusted by default and that verification is continuous, extending beyond mere entry points to encompass every transaction within the network. By implementing real-time monitoring and adaptive controls, StrongDM not only fortifies defenses against emerging threats but also enhances operational efficiency, setting a new standard in access control and security management tailored to the complexities of today's enterprises.
Top Features:
- Advanced Strong Policy Engine: Leveraging the sophisticated Cedar Policy Language, this engine enables ultra-fast policy assessments, ensuring that security mechanisms enhance rather than impede system performance. This results in robust, immediate access controls without sacrificing operational efficiency.
- Unified Policy Management: StrongDM revolutionizes policy oversight, offering a seamless, integrated framework that fortifies your entire digital ecosystem. This unified strategy not only simplifies administrative processes but also fortifies your security posture with layered, coherent protective measures.
- Versatile Authorization Schemes: Reflecting the diverse needs of modern organizations, StrongDM supports an array of authorization models, providing the versatility needed to design a security protocol that best fits your unique operational requirements.
- Detailed Control through Contextual Signals: Introducing context-sensitive indicators, such as geographical data or device integrity, empowers finer-grained, more informed access decisions. This ensures that access permissions are not just based on identity but are also influenced by situational factors, aligning more closely with Zero Trust principles.
- Enhanced Device Trust Framework: Incorporating device health into security evaluations, this feature extends the decision-making process beyond traditional metrics. Assessing the security posture of devices prior to granting access adds a critical layer of defense, elevating your overall security strategy.
StrongDM’s Zero Trust Customer Use Cases
- Clarity AI: With a fully remote workforce spread across multiple continents, Clarity AI faced a unique challenge: how to implement Zero Trust while maintaining a flexible, productive environment for its developers. The team at Clarity AI discovered StrongDM while researching how to implement Zero Trust. Read Clarity AI’s full story.
"We tested out StrongDM and other competitors. In the end, StrongDM was the one that fit our needs." – Luis Cuervo, IT and security manager at Clarity AI
- Beekeeper: By eliminating end-user credentials and leaning into Least Privilege with StrongDM, Beekeeper is on track to achieve its ultimate goal: Zero Trust. Read Beekeeper’s full story.

- Better.com: Better uses StrongDM to adopt zero trust access. Read Better.com’s full story.
StrongDM Pros
- Enhanced security through continuous verification
- Real-time response to threats
- Granular access control based on context
- Simplified compliance reporting
- 14-day trial
StrongDM Cons
- SaaS-only offering
- Requires continual access to StrongDM API for access to managed resources
Pricing Information
StrongDM offers simple pricing, including support for all resource types.
Users have the option to sign up for a free trial.
2. Twingate
Twingate markets its zero-trust network access platform as an alternative to business VPNs. It’s not hard to see how their solution beats out other VPNs measures of performance, ease of use, and security.Twingate’s centralized zero trust orchestration layer is deployable in about 15 minutes without altering IP addresses, remapping network names, or modifying firewall rules, and integrates out of the box with with major identity providers, MDM/EDRs, SIEMs, and DOH providers.
Twingate’s zero-trust access model features data encryption and split tunneling, creating, making traffic segregation relatively easy to implement. The product offers audit logging, and can detect and thwart anomalous access behaviors, adding extra security.
Eliminating exposure to the internet, Twingate’s solution can enforce least-privilege access policies via access filters applied at the application, rather than network, level. Add to that integrated multi-factor authentication and single sign-on capabilities, all in a user-friendly SaaS solution.
Twingate Pros
- Advanced security features
- Granular permissions
- Easy setup
- Secure infrastructure
- Multi-factor authentication
- Single sign-on
- Network access controls
- Apply Zero Trust to any resource, cloud-based or on-premises
- 14-day trial
Twingate Cons
- Designed to collect private data
- Command line interface only for Linux
- No self-hosted version
- Does not allow access control to servers at the port level
- No Linux GUI client
- Connectors require frequent, time-consuming manual updates
- Tiered pricing scheme
- Detailed auditing only available at the enterprise tier
3. JumpCloud Open Directory Platform
JumpCloud aims to be the all-in-one solution for zero trust identity and access management. Built on a foundation of open standards, its cloud-based Open Directory Platform enables management of all cross-OS server, device, and user identities, including single sign-on (SSO), conditional, and passwordless access, from a single pane of glass.
JumpCloud isn’t short on functionality or interoperability; it gives organizations choices about what tools they use, and when and how they can use them. They can connect and expand their chosen set of tools with generous options for integrations. For example, the platform integrates to popular tools and services, including AWS Identity Center, Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Active Directory, HRIS platforms, and network infrastructure resources.
If this all sounds a bit busy, JumpCloud suggests that integrations are easy, and once set up, each user has a single unified identity that connects them to their resources securely and without friction. For example, it’s possible to easily import user accounts from another identity source, like HR or an existing directory. Also, identity and access changes in one source automatically take effect across all connected resources.
As is often the case with expansive platform solutions, JumpCloud offers a comprehensive set of advanced functionalities and customization options. Some organizations may find these features rather complex to configure or manage, requiring additional time and resources for implementation and maintenance.
JumpCloud Open Directory Platform Pros
- Comprehensive platform with support for many integrations
- Flexibility in enforcement of access controls
- Access to AWS resources and 900+ pre-built applications
- Event logging and compliance reporting
- 30-day trial
JumpCloud Open Directory Platform Cons
- Tiered pricing
- Additional charges for some options
- Limited support for legacy or on-premises systems
- Learning curve
- Internet connectivity required
- Feature set complexity
4. Google BeyondCorp
BeyondCorp is the term for Google’s own Zero Trust network architecture. The company shifted the perimeter from the network to individual users, eliminating its old VPN-based approach to remote access. Over a decade, Google refined BeyondCorp into a full-scale, zero trust access control system -- and packaged it into its BeyondCorp Enterprise offering.
BeyondCorp is built on Google’s planet-scale network and infrastructure, which powers low-latency connections and elastic scaling. In everyday use, it offers many of the same features one would expect from a solid access control system. These include, for example, granular access control based on policies like user identity, device health, and other contextual factors; hybrid support for access to SaaS apps, web apps, client-server apps, and cloud resources in the cloud or on-prem; and integrated threat and data protection.
There are some special Google signatures in the service experience too. For example, it does not use software agents on end-user devices, instead relying on the Chrome browser as its source of endpoint data. Although Chrome leads the global browser market by a wide margin, this “lock in” to the Chrome browser may be an issue for some organizations.
Google BeyondCorp Pros
- Discounts for large deployments
- Fine-grained access control
- Advanced security features
- SSO, access control policies, access proxy, and user- and device-based authentication
- 14-day trial
Google BeyondCorp Cons
- Compatibility with legacy and third-party technologies may be lacking
- Reliance on Chrome and Google’s ecosystem
- Cloud-based subscription service with no self-hosted option
5. Microsoft Azure Entra ID
Microsoft Azure Entra ID, formerly Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), is a cloud-based identity and access management service offered by Microsoft as part of its Azure cloud platform.
While Entra ID is separate from on-premises Active Directory, they can coexist in hybrid environments. Entra ID allows users to securely access external resources such as Microsoft 365, the Azure portal, and thousands of other SaaS applications, as well as internal resources like apps on the corporate intranet.
Subscribers to Microsoft's cloud services, like Azure, 365, and others, automatically gain access to Entra ID, or it can be purchased as a stand-alone service. The solution offers advanced features for managing identity and access, including built-in MFA, single sign-on (SSO), B2B collaboration controls, self-service password setting, and centralized management of identities and access, in the cloud or on-premises, for improved visibility and control. Entra integrates with Microsoft productivity tools and cloud storage (Office 365, OneDrive, etc.) as well as third- party services.
Microsoft Azure Entra ID Pros
- Easy integration with other Microsoft products
- Passwordless sign-on options
- Included with Microsoft cloud subscriptions
- Conditional access policies based on roles, device compliance, network location, and so forth
- Setup, especially when integrating with on-prem AD, may be complex
- 30-day trial
Microsoft Azure Entra ID Cons
- Contextual access to MFA restricted to premium tier
- No user SSO application
- Tiered pricing, with advanced functionalities such as self-service and mobile device security requiring upgrade
- Dependency on Microsoft ecosystem may affect use of non-Microsoft applications and platforms
6. OKTA Identity Cloud
Okta aims for flexibility and neutrality in Identity Cloud, its cloud-based IAM solution. It comes in two varieties: Customer Identity Cloud and Workforce Identity Cloud. On top of these foundational clouds, and in keeping with its focus on openness and choice, it offers a large a la carte menu of advanced IAM add-ons.
Okta typically gets good marks from IT for ease of setup and from end-users for user experience. It offers a high degree of MFA customization, with multiple authorization levels possible for applications and also at the organizational level. Organizations can set contextual or conditional MFA, triggered by the detection of new devices, IPs or other conditions, for example.
The company appears to be staying on top of the latest trends in access and authentication. For example, its MFA feature supports Apple TouchID and Windows Hello, and it is even using AI to improve its Identity Clouds.
One downside to Okta may be its pricing. Its menu of functionality is long, and adding features one by one can drive the bill up to as high as $15 per user per month.
OKTA Identity Cloud Pros
- SSO with custom org URLs and SIEM integration
- Okta Verify OTP
- User self-service portal
- Built-in integrations
- User SSO app
- Security reporting
- Passwordless sign-on options
- 30-day trial
OKTA Identity Cloud Cons
- A la carte functionality menu can lead to price creep
- Somewhat limited to web login management; not as suitable for complex developer environments
- No on-premises option
7. Zscaler
Zscaler stakes its claim in the zero trust space with its Zero Trust Exchange (ZTE) platform. ZTE routes all traffic through a global network of over 150 Zero Trust Exchanges, shielding it from network exposure. This secures access to private apps while minimizing latency. Zscaler’s ZTE manages security and network operations for users, workloads, IoT/OT, and B2B partners.
Zscaler's integrated security stack prevents unauthorized access with SWG, cloud firewall, DLP data loss prevention), sandboxing, and SSL inspection. It also employs machine learning for threat detection, inspecting all traffic—including encrypted traffic—for malicious content. Microtunneling: establishing secure connections for individual user requests.
The company emphasizes context in access security. The Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) service secures access to private applications (on-premises or in a public cloud) and services while providing an advanced network security layer. Its Policy Engine dynamically adapts authorization based on user location, device type, application access history, and threat intelligence. ZTE also integrates with existing Identity and IAM solutions and IDPs.
Reviewers have noted that of the 150 Point-of-Presence (PoP), ZPA is available in just 50 locations. Since user data must be sent back to a PoP before reaching the corporate data center, greater latency can result. Also, these PoPs are actually VMs hosted on Amazon Web Services, so they can’t control routing or scale resources to meet demand.
Zscaler Pros
- Customizable, granular access controls
- Advanced security
- Good visibility over assets and users
Zscaler Cons
- Pricing requires consultation
- Fast internet is needed for proper functioning
- The advertised number of PoPs may not apply to all services
- No free trial
8. BeyondTrust
BeyondTrust, formerly Bomgar, offers numerous zero trust solutions for identity and access management and endpoint security. While it does cover most of the bases in zero trust, it does so in a piecemeal fashion that can raise overall costs and complicate implementation.
Let’s run down the list of tools offered under the BeyondTrust brand name. Endpoint Privilege Management lets users approve and revoke access to critical systems while providing an audit trail. Password Safe manages access to and use of privileged credentials and SSH keys. DevOps Secret Safe also centralizes secrets management but utilizes REST APIs and CLI tools to streamline dev workflows and seamlessly integrate APIs. Privileged Remote Access secures access to workstations, including internal and external cloud infrastructure, eliminating the need for a VPN. Lastly, Remote Support allows IT to remotely monitor, access, and control any customer devices on or off the corporate network.
These tools are relatively easy to use on their own, but it’s worth noting that none of them add up to a single comprehensive zero trust solution. When combining them to implement zero trust through their whole IT environment, customers may find getting them all to work together or with existing tools is not exactly simple. Also, pricing can become confusing or run high.
BeyondTrust Pros
- SSH and RDP are available
- Manage permissions with AD, LDAPS, RADIUS & Kerberos
- Extends Microsoft AD authentication, SSO, & Group Policy Configuration Management to Unix/Linux
- 14-day trial
BeyondTrust Cons
- No comprehensive solutions
- Need to purchase add-ons
- Complex initial setup
- Very high licensing costs
9. Delinea
Delinea offers a range of zero trust solutions, including Privilege Manager, Server Suite, and Cloud Suite. Its flagship product, Secret Server, is a PAM solution that allows users to secure and manage all privileged accounts through a single dashboard. It has features for discovery, search, management, provisioning, and access.
Privilege Manager is an endpoint least privilege and application control solution for Windows and macOS. It can mitigate modern security threats like malware by removing local administrative rights from endpoints.
Cloud Suite is a unified PAM platform for privileged access management in multi-cloud environments. It enables users to enforce PAM policies dynamically, consolidate identities, and leverage directory services such as AD, OpenLDAP, and Azure AD.
Some reviewers have noted that deployment can be complex, and some common PAM requirements in Secret Server require customization through PowerShell, a task automation and configuration management program from Microsoft, which customers will have to purchase.
Additionally, Delinea's Privilege Manager lacks support for securing modern and cloud-native databases, Kubernetes clusters, cloud CLIs, switches, routers, or internal web applications, potentially limiting its applicability in certain environments.
Delinea Pros
- Available on premises and in the cloud
- Competitive pricing
- SSH access is available
- RDP access
- Authenticates users through LDAP and Active Directory (AD)
- Cloud and on-premise deployable
- 30-day trial
Delinea Cons
- Designed for legacy systems (AD, LDAP) and highly privileged administrators
- Not designed for cloud-native environments or newer database management systems
- Not designed for modern infrastructure tooling like Kubernetes, Docker, and ephemeral environments
- Does not cover all users, most of whom require access to systems with privileged data
- Does not secure access to modern and cloud-native databases, Kubernetes clusters, cloud CLIs, switches, routers, or internal web applications.
- Complex pricing
How to Choose The Right Zero Trust Security Solution
So what’s the best zero trust solution? There isn’t one -- at least not for all organizations, with their unique infrastructure, organizational structure, assets, and levels of protection needed. That said, asking some key questions can help them quickly find the best possible zero trust solution for them and weed out the rest.
Here are eight main points to consider when shopping for a zero trust solution.
- Assess Your Organization's Needs
- Look at your current cybersecurity posture, including existing infrastructure, data sensitivity, regulatory compliance requirements, and risk tolerance.
- Identify Key Objectives
- What do you aim to accomplish with a zero trust solution?
- Common goals include: Improve access controls, enhance threat detection capabilities, simplify compliance management, and reduce security risks.
- Evaluate Available Solutions
- Consider features, scalability, ease of deployment and management, integration capabilities, vendor reputation, and customer support.
- Don’t hesitate to ask salespeople questions.
- Understand Technical Requirements
- Ask about compatibility with existing systems and applications, support for multiple devices and platforms, and ability to accommodate future growth and changes.
- Is it deployable on premises, in the cloud, or both?
- Consider User Experience
- Assess the user experience offered by the solution, both for administrators and end-users.
- Will the solution impact operational efficiencies or productivity?
- Cost Considerations
- Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the solution, including upfront costs, maintenance, licensing or subscription fees, and so forth.
- Vendor Reputation and Support
- Select a reputable vendor with verified track record.
- Check out customer reviews, case and testimonials online.
- What kind of support does the vendor offer?
- Pilot and Test
- Consider a free trial to test the solution in a controlled environment or conduct a proof-of-concept (POC) before making a full deployment.
The difference between failure and success
Going through these steps before choosing a zero trust solution for a full deployment can prevent your organization from wasting time, money, and effort on projects that ultimately fail.
Ask the right questions upfront, and you’ll have a much better chance of a smooth, no-surprises deployment and project success.
Achieve True Zero Trust Security with StrongDM
Remember the true meaning of zero trust. It’s not just a marketing term. Achieving real zero trust security requires a paradigm shift from static, perimeter-based models to dynamic, context-aware systems that put identity first. For that, you need zero trust principles built into the foundation of your solution.
StrongDM embodies the zero trust model in the features and capabilities that protect its users’ most sensitive assets on a daily basis. It puts zero trust into practice with robust security controls that adapt in real-time to potential threats, support for versatile authorization schemes, and fine-grained control through contextual signals.
Its advanced monitoring and adaptive policies not only defend against ever-evolving threats but also enhance operational efficiency, setting a new standard in access control and security for modern enterprises. With StrongDM, customers can implement zero trust in the most beneficial way possible for their organizations.
Want to see StrongDM in action? Book a demo.
Next Steps
StrongDM unifies access management across databases, servers, clusters, and more—for IT, security, and DevOps teams.
- Learn how StrongDM works
- Book a personalized demo
- Start your free StrongDM trial

Categories:

About the Author
John Martinez, Technical Evangelist, has had a long 30+ year career in systems engineering and architecture, but has spent the last 13+ years working on the Cloud, and specifically, Cloud Security. He's currently the Technical Evangelist at StrongDM, taking the message of Zero Trust Privileged Access Management (PAM) to the world. As a practitioner, he architected and created cloud automation, DevOps, and security and compliance solutions at Netflix and Adobe. He worked closely with customers at Evident.io, where he was telling the world about how cloud security should be done at conferences, meetups and customer sessions. Before coming to StrongDM, he lead an innovations and solutions team at Palo Alto Networks, working across many of the company's security products.
You May Also Like