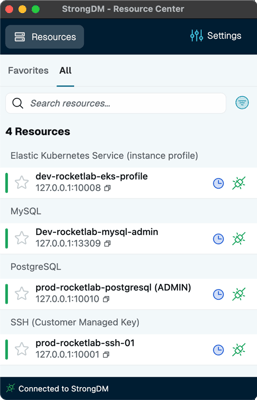
When working with or administering a database, you'll need to delete, remove, or drop users at some point. This might seem like a routine task, but dropping unnecessary or old users is crucial for maintaining database security. This helps remove access points for malicious actors — both in-house and external — so only authorized individuals can perform operations on it.
Posts by Category:
- Security
- Access
- DevOps
- Privileged Access Management
- Auditing
- Zero Trust
- Compliance
- Policy
- Databases
- SOC 2
- Authentication
- Identity and Access Management
- Team
- Compare
- Engineering
- Integrations
- Product
- Kubernetes
- AWS
- Productivity
- Podcasts
- SSH
- Observability
- HIPAA
- ISO 27001
- Role-Based Access Control
- Dynamic Access Management
- Secure Access Service Edge
- Webinars
- Events
- NIST
- Onboarding
- Passwordless
- Offsites
- Platform
- PCI
As enterprises increasingly migrate workloads to the cloud, security strategies must adapt to meet evolving threats. Zero Trust, emphasizing identity verification and least privilege access, has become a critical framework for securing cloud environments. StrongDM’s recent survey of 600 cybersecurity professionals sheds light on the progress and challenges organizations face in adopting Zero Trust for the cloud.

In this guide, we’ll cover the 15 most important cybersecurity regulations for financial services providers. We’ll show exactly which ones—from GDPR and PCI DSS to MAS TRM, CBEST, and others—apply to your organization, and explain, in plain in English, what they are, how they impact your business, and how you can initiate a path for compliance.
The HIPAA Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) requirement is a security measure that requires users to verify their identity using at least two different factors—such as something they know (a password), something they have (a smartphone or token), or something they are (a fingerprint)—to access systems containing electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). This additional layer of security is designed to protect sensitive healthcare data from unauthorized access, even if one credential is

I’ll spare you the “I drink your milkshake” tropes, but we all face a sobering reality: there will be breaches in 2025. Breaches aren’t a question of “if” anymore—they’re a question of “when” and “how bad.” It’s a foregone conclusion, like taxes or the 37th season of Grey’s Anatomy. But here’s the good news: knowing the inevitability of breaches gives us the perfect opportunity to prepare, if we have the will – and strategy – oh, and tools – to do it. And no, I’m not talking about the “build a

In this post, we’ll explore what PSD2 compliance challenges businesses face, and how StrongDM simplifies secure access to help organizations confidently meet PSD2 requirements.
Managing access to critical infrastructure is a challenge for many organizations. Legacy tools often struggle to keep up, creating inefficiencies, security gaps, and frustration. StrongDM offers a modern solution that simplifies access management, strengthens security, and improves workflows. In this post, we’ll explore 13 real-world examples of how StrongDM helps teams solve access challenges and achieve their goals.

Having a complete view of all your databases in PostgreSQL is essential for effective database management. This guide explores six proven methods you can use to quickly list all of your databases.

Connecting to a remote PostgreSQL database can prove daunting for some teams. Your organization risks losing valuable time, which then leads to lost productivity. Thankfully, there are four different ways to connect to a remote PostgreSQL database and improve your team's efficiency.

Network Level Authentication (NLA) is a security feature of Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) that requires users to authenticate before establishing a remote session. By enforcing this pre-authentication step, NLA reduces the risk of unauthorized access, conserves server resources, and protects against attacks like credential interception and denial of service. While effective in securing RDP sessions, NLA is limited to a single protocol, lacks flexibility, and can add complexity in

Learn the step-by-step approach to creating a database in PostgreSQL. Our in-depth guide explores two main methods—using psql and pgAdmin.

Enterprises seek ways to effectively address the needs of dynamic, always-evolving cloud infrastructures, and StrongDM has developed a platform that is designed with built-in capabilities to support continuous compliance in AWS environments.
![IP Whitelisting: Meaning, Alternatives & More [2026 Guide]](https://discover.strongdm.com/hubfs/ip-whitelisting.jpg)
IP whitelisting is a security strategy that restricts access to a network/system to a specified list of trusted IP addresses. This approach ensures that only individuals using the approved addresses can access certain resources.